Class 9 - Science
Chapter 2 - Is Matter Around Us Pure

Top Block 1
Take the steam that is coming out of a boiling water and allow it to cool down, it condenses to form water and on further cooling of this water we get ice.
(3) On applying pressure and reducing temperature we can liquefy gases or change them into solid.
Example: Take carbon-dioxide gas, reduce its temperature and apply lot of pressure on it so that it changes into solid carbon dioxide, called diy ice, which is used as refrigerant for cooling.
If the pressure on it is decreased it directly changes into gas.
In LPG cylinders, the petroleum gas is cooled and with lot of pressure changes it into liquid state.
While using this LPG, we release the pressure exerted on it and hence it comes out in the form of gas.
Question 2. Explain giving examples the various factors on which rate of evaporation depends.
Answer :
The rate of evaporation depends on the following factors:
(1) Surface area: If the surface area is increased the rate of evaporation also increases.
(a) To dry the clothes we spread them to dry faster.
(b) Tea in saucer cools faster than in a cup.
(2) Temperature: If the temperature is increased the rate of evaporation also increases. Due to increase in temperature the particles gain more kinetic energy and change their phase from liquid to gaseous. Water will evaporate faster in sun than in shade.
(3) Humidity: It is the amount of water vapour present in air. The air can hold definite amount of water vapour, at a given temperature. If the amount of water vapour is high in the air then the rate of evaporation decreases. On hot and humid day, desert coolers are not effective as the air cannot hold any more moisture to get the cooling effect.
(4) Wind speed: With the increase in wind speed, the rate of evaporation increases. The particles of water vapour move away with the wind, decreasing the amount of water vapour in the surrounding.
V. Value-Based Questions in Science for Class 9
Question 1. Adil parked his bicycle on a sunny day in a parking stand of his school campus. When the school got over Adil saw his burst cycle type. Thereafter he kept less air in his cycle types and did not inflate them fully.
(a) Why did the type burst?
(b) Why is air compressible?
(c) What value of Adil is reflected in the above act?
Answer :
(a) The tyre burst because the air inside the tyre got heated and therefore exerted pressure on the walls of the tyre.
(b) Air is compressible because it has large intermolecular space.
(c) Adil showed the value of intelligence, awareness and self responsibility.
Question 2. Akshay’s friend visited his house in Mumbai and he was surprised to see air conditioners installed in all of his rooms. His friend advised Akshay to use water-coolers and save electricity. On this Akshay told, him that the water-cooler is not at all effective in coastal areas.
(a) Why are water-cooler not effective in coastal areas?
(b) What are the other two factors on which evaporation of water depends?
(c) What value of Akshay’s friend is seen in this act?
Answer :
(a) Water coolers are not effective in coastal areas due to high rate of humidity.
(b) The other two factors on which evaporation of water depends are temperature and surface area.
(c) Akshay’s friend showed the value of concerned citizen, morally responsible and friendly in nature.
Question 3. Sita lived in a village and could, not afford refrigerator in her house. She knew how to keep water cold and preserve all perishable items in her house. She kept ivet cloth surrounding the earthen pot to keep water cool, she also kept vegetables fresh by keeping them in wet gunny bag and timely sprinkled water over it.
(a) Why did Sita keep wet cloth surrounding the earthen pot?
(b) Suggest one more method of keeping the house cool in summer.
(c) What value of Sita is reflected in the above case?
Answer :
(a) The wet cloth gave the cooling effect to the pot, as the water in the cloth evaporated and evaporation causes cooling effect.
(b) By sprinkling some water on the lawn/veranda of the house can keep the house cool.
(c) Sita showed the value of responsible behaviour.
Question 4. Shreya commutes in a CNG fitted van to school every day along with many other students. She told the van driver to get the CNG connection certified and timely checked it for any leakage or loose connection of pipes. She told the driver to be more careful during summers.
(a) What is CNG?
(b) Why should one be more careful with CNG cylinders during summer?
(c) What value of Shreya is seen in the above act?
Answer :
(a) CNG is Compressed Natural Gas used as fuel.
(b) During summers, the CNG connections and cylinder need to be checked because the gas expands due to heat and if there would be any leakage then it would cause fire in the vehicle.
(c) Shreya showed the value of concerned citizen and morally responsible behaviour.
Class 9 Science NCERT Textbook solutions with NCERTworld.com Page 24
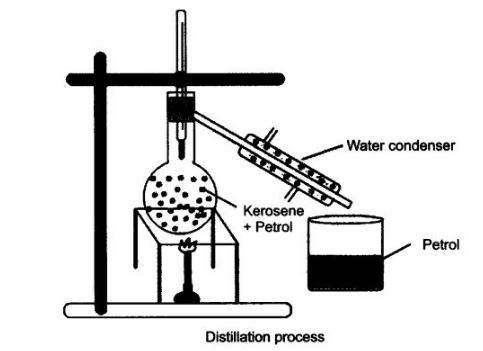
Question 1. How will you separate a mixture containing kerosene and petrol (difference in their boiling points is more than 25°C), which are miscible with each other?
Answer :
A mixture of kerosene and petrol which are miscible with each other can be separated by distillation.
Method
- Take a mixture in a distillation flask.
- Fit it with a thermometer.
- Arrange the apparatus as shown in the figure.
- Heat the mixture slowly.
- Petrol vaporises first as it has lower boiling point. It condenses in the condenser and is collected from the condenser outlet.
- Kerosene is left behind in the distillation flask.
Mddle block 1
Question 2. Name the technique to separate
(i) butter from curd,
(ii) salt from sea-water,
(iii) camphor from salt.
Answer :
(i) Centrifugation,
(ii) Evaporation,
(iii) Sublimation.
Question 3. What type of mixtures are separated by the technique of crystallisation?
Answer :
Crystallisation technique is used to purify solid with some impurities in it. Example: Salt from sea-water.
Class 9 Science NCERT Textbook solutions with NCERTworld.com : Page 24
Question 1. Classify the following as chemical or physical changes:
- cutting of trees,
- melting of butter in a pan,
- rusting of almirah,
- boiling of water to form steam,
- passing of electric current, through water and the water breaking down into hydrogen and oxygen gas,
- dissolving common salt in water,
- making a fruit salad with raw fruits and
- burning of paper and wood.
Answer:
| Physical Changes | Chemical Changes |
|---|---|
| 1. Cutting of trees | Rusting of Almirah |
| 2. Melting of butter in a pan | Passing of electric current through water and than breaking down into hydrogen and oxygen gas |
| 3. Boiling of water to form steam | Burning of paper and wood |
| 4. Dissolving common salt in water | |
| 5. Making a fruit salad with raw fruits. | E. |
Question 2. Try segregating the things around you as pure substances or mixtures
Answer :
Pure substances—Water, bread, sugar and gold.
Mixtures—Steel, plastic, paper, talc, milk and air.
Questions From NCERT Textbook for Class 9 Science
Question 1. Which separation techniques will you apply for the separation of the following?
(a) Sodium chloride from its solution in water.
(b) Ammonium chloride from a mixture containing sodium chloride and ammonium chloride.
(c) Small pieces of metal in the engine oil of a car.
(d) Different pigments from an extract of flower petals.
(e) Butter from curd.
(f) Oil from water.
(g) Tea leaves from tea.
(h) Iron pins from sand.
(i) Wheat grains from husk.
(j) Fine mud particles suspended in water.
Answer :
(a) Evaporation
(b) Sublimation
(c) Filtration
(d) Chromatography
(e) Centrifugation
(f) Separating funnel
(g) Filtration
(h) Magnetic separation
(i) Winnowing/ sedimentation
(j) Decantation and filtration
Question 2. Write the steps you would use for making tea. Use the words, solution, solvent, solute, dissolve, soluble, insoluble, filtrate and residue.
Answer :
1. Take a cup of water in a container as solvent and heat it.
2. Add sugar in it which is solute. Heat it till all sugar dissolves.
3. You get a solution of water and sugar.
4. Sugar is soluble in water completely.
5. Add half a tea-spoon of tea-leaves, it is insoluble in water.
6. Boil the content, add milk which is also soluble in water, boil again.
7. Filter the tea with the help of strainer, the tea collected in cup is filtrate and the tea leaves collected on the strainer is residue.
Question 3. Pragya tested the solubility of three different substances at different temperatures and collected, the data as given below (results are given in the following table, as grams of substance dissolved in 100 grams of water to form a saturated solution).
| Substance Dissolved | Temperature in K and Solubility | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 283 | 293 | 313 | 333 | 353 | |
| Potassium Nitrate | 21 | 32 | 62 | 106 | 167 |
| Sodium Chloride | 36 | 36 | 36 | 37 | 37 |
| Potassium Chloride | 35 | 35 | 40 | 46 | 54 |
| Ammonium Chloride | 24 | 37 | 41 | 55 | 66 |
(a) What mass of potassium nitrate would be needed to produce a saturated solution of potassium nitrate in 50 grams of water at 313 K?
(b) Pragya makes a saturated solution of potassium chloride in water at 353 K and leaves the solution to coo! at room temperature. What would she observe us the solution cools? Explain.
(c) Find the solubility of each salt at 293 K. Which salt has the highest solubility at this temperature?
(d) What is the effect of change of temperature on the solubility of a salt?
Answer :
(a) Mass of KNO3 to produce a saturated solution of KNO3in 100 grams of water at 313 K = 62 g
∴Mass of KNO3 in 50grams of water at 313 K
= (620 x 50)⁄100 = 31.0 g
(b) Crystals of Chloride will be obtained on cooling the saturated solution.
(c) Solubility of each salt at 293 K is
(i) Potassium Nitrate → 32 g
(ii) Sodium Chloride → 36 g
(iii) Potassium Chloride → 35 g
(iv) Ammonium Chloride → 37 g
Question 4. Explain the following giving examples:
(a) Saturated solution
(b) Pure substance
(c) Colloid
(d) Suspension
Answer :
(a) Saturated solution: In a given solvent when no more solute can dissolve further at a given temperature is called saturated solution.
(b) Pure substance: A pure substance consists of a single type of particles. E.g., gold, silver.
(c) Colloid: A colloid is a solution in which the size of solute particles are bigger than that of true solution. These particles cannot be seen with our naked eyes, they are stable, e.g., ink, blood.
(d) Suspension: It is a heterogeneous mixture in which the solute particles are big enough to settle down, e.g., chalk-water, paints, etc.
Question 5. Classify each of the following as a homogeneous or heterogeneous mixture: soda water, wood, air. soil, vinegar, filtered tea.
Answer :
Homogeneous: Soda water, vinegar, filtered tea.
Heterogeneous: Wood, air, soil.
Question 6. How would, you confirm that a colourless liquid given to you is pure water?
Answer :
By finding the boiling point of a given colourless liquid. If the liquid boils at 100°C at atmospheric pressure, then it is pure water. This is because pure substances have fixed melting and boiling point.
Question 7. Which of the following materials fall in the category of a “pure substance”?
(a) Ice (b) Milk (c) Iron
(d) Hydrochloric acid (e) Calcium oxide (f) Mercury
(g) Back (h) Wood (i) Air.
Answer :
Pure substances are: Ice, iron, hydrochloric acid, calcium oxide and mercury.
Question 8. Identify the solutions among the following mixtures.
(a) Soil
(b) Sea water
(c) Air
(d) Coal
(e) Soda water.
Answer :
Solutions are: Sea water soda water and air.
Question 9. Which of the following will show “Tyndall effect”?
(a) Salt solution
(b) Milk
(c) Copper sulphate solution
(d) Starch solution.
Answer :
Milk and starch solution.
Question 10. Classify the following into elements, compounds and mixtures.
(a) Sodium (b) Soil (c) Sugar solution
(d) Silver (e) Calcium carbonate (f) Tin
(g) Silicon (h) Coal (i) Air
(j) Soap (k) Methane (l) Carbon dioxide
(m) Blood
Answer :
Elements – Compounds – Mixtures
Sodium – Calcium carbonate – Sugar solution
Silver – Methane – Soil
Tin – Carbon dioxide – Coal
Silicon – Soap – Air ,Blood
Question 11. Which of the following are chemical changes?
(a) Growth of a plant
(b) Rusting of iron
(c) Mixing of iron filings and sand
(d) Cooking of food
(e) Digestion of food
(f) Freezing of water
(g) Burning of a candle.
Answer :
Chemical changes are:
(a) Growth of a plant (b) Rusting of iron
(c) Cooking of food (d) Digestion of food
(e) Burning of a candle
MORE QUESTIONS SOLVED
I. Multiple Choice Questions
Choose the correct option:
1. Fog, clouds are an example of
(a) aerosol
(b) colloid
(c) suspension
(d) emulsion
2. Sponge can be compressed, it is a
(a) solid
(b) liquid
(c) gas
(d) foam
3. An impure sample of potash alum can be purified by
(a) evaporation
(b) crystallisation
(c) centrifugation
(d) filtration
4. Chalk dissolved in water is an example of
(a) true solution
(b) colloid
(c) suspension
(d) saturated solution
5. 50 gm sugar is dissolved in a glass of water at 30°C. On heating this solution it will
(a) crystallise
(b) evaporate
(c) become unsaturated
(d) sugar will char
6. Which of the following shows tyndall effects?
(a) salt solution
(b) sugar solution
(c) starch solution
(d) copper sulphate solution
7. Pick up the odd one out.
(a) brass
(b) air
(c) sand
(d) graphite
8. Which of the following is liquid-liquid solution?
(a) face-cream
(b) emulsion
(c) milk
(d) all of these
9. To separate two miscible liquids by fractional distillation, it should have one of the following condition
(a) should be miscible
(b) should be immiscible
(c) difference in the boiling point should be less than 25 K
(d) none of these
10. To obtain toned and double toned milk from full-cream milk we can
(a) filtrate it
(b) sediment it
(c) distillate it –
(d) centrifuge it
11. The separation technique which involves the difference in their densities is
(a) sublimation
(b) separation by separating funnel
(c) centrifugation
(d) both (b) and (c)
Answer :
1—(a). 2—(a), 3—(b), 4—(c), 5—(c), 6—(c), 7—(d), 8—(d), 9—(c), 10—(d), 11-(d).
I. Very Short Answer Type Questions in Class 9 Science Chapter 2 Is Matter Around Us Pure
Question 1. Define solvent.
Answer :
The component of the solution that dissolves the other component in it is called the solvent.
Question 2. Define solute.
Answer :
The component of the solution that is dissolved in the solvent is called solute.
Question 3. What is ‘tincture of iodine’?
Answer :
A solution of iodine in alcohol is known as tincture of iodine. It has iodine (solid) as the solute and alcohol (liquid) as the solvent.
Question 4. What are alloys?
Answer :
The homogeneous mixture of two or more metals or a metal and non-metal is called an alloy. E.g., steel is an alloy of iron and carbon.
Question 5. Give one example of gas in liquid solution.
Answer :
Cold-drinks, carbon dioxide gas as solute is mixed with water as a solvent.
Question 6. How can a solution be dilute or concentrated?
Answer :
The amount of solute dissolving in a solvent decides whether the solution is dilute or concentrated.
Question 7. What is “concentration of a solution”?
Answer :
The concentration of a solution is the amount of solute present in a given amount of solution or the amount of solute dissolved in a given mass or volume of solvent.
Question 8. State the difference between aqueous and, non-aqueous solution.
Answer :
Aqueous solutions have water as solvent and non-aqueous solutions do not haVe water as solvent.
Question 9. What is “solubility” of a solute?
Answer :
The amount of the solute present in the saturated solution at the given temperature is called its solubility.
Question 10. What is saturated solution?
Answer :
The maximum amount of solute dissolved in a solvent at given temperature is called saturated solution, where no more solute can dissolve further.
Question 11. What is unsaturated solution?
Answer :
If the amount of solute contained in a solution is less than the saturation level, it is called an unsaturated solution.
Question 12. How can you convert saturated solution into unsaturated or vice-versa?
Answer :
Saturated solution on heating becomes unsaturated and unsaturated solution on cooling becomes saturated.
Question 13. Why water is called universal solvent?
Answer :
Water can dissolve large number of substances in it.
Question 14. What is Tyndall effect?
Answer :
The scattering of light by colloidal particles is known as Tyndall effect.