Class 10 - Science
Chapter 3 - Metals and Non-metals

Top Block 1
Question : 1
What are amphoteric oxides? Give two examples of amphoteric oxides.
Answer :
Amphoteric oxides are the oxides, which react with both acids and bases to form salt and water. E.g.ZnO andAl2O3.
Question : 2
Name two metals, which will displace hydrogen from dilute acids, and two metals which will not.
Answer :
Very reactive metals like Zn and Mg displace hydrogen from dilute acids. On the other hand less reactive metals like Cu, Ag, etc. do not displace hydrogen from dilute acids.
Question : 3
In the electrolytic refining of a metal M, what would you take as the anode, the cathode and the electrolyte?
Answer :
Anode is impure, thick block of metal M.
Cathode is a thin strip/wire of pure metal M.
Electrolyte is a suitable salt solution of metal M.
Question : 4
State two ways to prevent the rusting of iron.
Answer :
By coating the surface of iron by rust proof paints.
By applying oil or grease to the surface of iron objects so that supply of air consisting of moisture is cut off from the surface.
Question : 5
What types of oxides are formed when non-metals combine with oxygen?
Answer :
When non-metals combine with oxygen it forms either neutral or acidic oxides. CO is a neutral oxide; N2O5orN2O3 is an acidic oxide.
Question : 6 Give reason
i. Metals replace hydrogen from dilute acids, whereas non-metals do not.
ii. Carbonate and sulphide ores are usually converted into oxides during the process of extraction.
Answer :
i. Metals are electropositive in nature. They readily lose electrons. These electrons reduce the protons liberated from the acid to liberate hydrogen gas, whereas non-metals possess a tendency to gain electrons and hence they do not furnish electrons to protons liberated from acids. Hence H2 gas is not liberated.
ii. As it is easier to reduce metal oxides to metal, prior to reduction, metal sulphides and carbonates must be converted to oxides.
Question : 7
Differentiate between metals and non-metals on the basis of their chemical properties.
Answer :
| Metals | Non – Metals |
|---|---|
| Metals on heating with oxygen form ionic oxides, which are basic in nature and which dissolve in water to form bases, which turn red litmus blue | Non-metals on heating with oxygen form covalent oxides which are acidic in nature and dissolve in water to form acids, which turn blue litmus red |
| Metals are reducing agents | Non-metals are good oxidizing agents |
| All are solid except murcury | Solid – Liquid – gaseous |
| Lustrous | Non-lustrous except graphite except graphite |
| Conductor of electricity and heat | Non-Conductor of electricity and heat |
| Electro positive. Losses electrons readily and becomes a positive ion | Electro negative. Gains electrons readily and becomes a Negative ion |
Question : 8 Explain why the surface of some metals acquires a dull appearance when exposed to air for a long time.
Answer :
This is due to the surface oxidation of metals when exposed to moist air. For e.g. copper turns green on its surface due to the formation of basic copper carbonate Cu(OH)2. CuCO3. Similarly silver becomes black due to the formation of black Ag2S and Aluminium forms a white coating of Al2O3 on its surface.
Question : 9 State which of the following metals would give hydrogen when added to dilute hydrochloric acid.
i. Iron, ii. Copper iii. Magnesium
Answer :
Copper does not react with dilute hydrochloric acid at all. This shows that copper is even less reactive than iron.
Fe + 2HCl ——→ FeCl2 + H2
Mg + 2HCl ——→ MgCl2 + H2
Cu + HCl——→ No reaction
Question : 10 Name a non-metallic element, which conducts electricity.
Answer :
Carbon in the form of graphite conducts electricity, as there is a free electron in each carbon atom, which moves freely in between the hexagonal layers.
Question : 11 Which metals do not corrode easily?
Answer :
Gold and platinum and other noble metals do not corrode in air.
Question : 12 What are alloys?
Answer :
Alloys are homogeneous mixtures of two or more metals, or a metal and a non-metal.E.g.Steel, brass, bronze, etc.
Question : 13 Define the following terms.
(i) Minerals
(ii) Ores
(iii) Gangue
Answer :
(i) Minerals
All compounds or elements, which occur naturally in the earth’s crust, are called minerals. Example: Alums, K2SO4.Al2(SO4)3 . 24 H2O, Bauxite Al2O3.2H2O
(ii) Ores
Those minerals from which a metal can be profitably extracted are called ores. Bauxite (Al2O3.2H2O) is the ore of Al, copper pyrite CuFeS2. All minerals are not ores but all ores are minerals.
(iii) Gangue
When an ore is mined from the earth, it is always found to be contaminated with sand rocky materials. The impurity of sand and rock materials present in the ore is known as gangue.
Question : 14 Name two metals that are found in nature in the free state.
Answer :
Gold and platinum are found in the free state in nature.
Question : 15 What is chemical process used for obtaining a metal from its oxide?
Answer :
ZnO + C ——→ Zn + CO
PbO + C ——→ Pb + CO
Question : 16 Name two metals, which can form hydrides with metals.
Answer :
Sodium and calcium form stable hydrides on reacting with hydrogen.
Question : 17 Does every mineral have a definite and a fixed composition? Explain.
Answer :
Yes, every mineral has a definite and a fixed composition. Minerals are widely distributed in the earth’s crust in the form of oxides, carbonates, sulphides, sulphates, nitrates, etc. These minerals are formed as a result of chemical changes taking place during the formation of earth.
Question : 18 Explain the meaning of malleable and ductile.
Answer :
Malleable is being able to be beaten/hammered into thin sheets.
Ductile is being able to be drawn into thin wires.
Question : 19 i. Write the electron don structures for sodium, oxygen and magnesium
ii. Show the formation of MgO and Na2O by the transfer of electrons.
iii. What are the ions present in these compounds?
Answer :
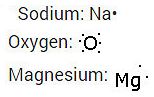
When magnesium reacts with oxygen, the magnesium atom transfer its two outermost electrons to an oxygen atom. By losing 2 electrons, the magnesium atoms from a magnesium ion (Mg2+) and by gaining 2 electrons the oxygen atom forms an oxide ion(O2)
Mddle block 1
Two sodium atoms transfer their 2 outermost electrons to an oxygen atom. By losing two electrons, the two sodium atoms form two sodium ions (2Na+). And by gaining two electrons, the oxygen atom forms an oxide ion(O2-)
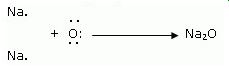
The ions present in Magnesium oxide compound (MgO) are magnesium ions (Mg2+) and oxide ion(O2)
Question : 20 You must have seen tarnished copper vessels being cleaned with lemon or tamarind juice. Explain why these sour substances are effective in cleaning the vessels.
Answer :
The sour substances such as lemon (or tamarind juice) contain acids. These acids dissolve the coating of copper oxide or basic copper carbonate present on the surface of tarnished copper vessels and make them shining red-brown again.
Question : 21 Give an example of a metal which-
i. is a liquid at room temperature.
ii. can be easily cut with a knife.
iii. is the best conductor of heat.
iv. is a poor conductor of heat.
Answer :
i. Mercury is in liquid state at room temperature.
ii. Sodium and potassium are soft metals which can be easily cut with a knife.
iii. Silver is the best conductor of electricity.
iv. Mercury is a poor conductor of heat.
Question : 22 Why is sodium kept immersed in kerosene?
Answer :
Sodium metal is kept immersed in kerosene to prevent their reaction with oxygen, moisture and carbon dioxide of air.
Question : 23 Why do ionic compounds have high melting points?
Answer :
These compounds are made up of positive and negative ions. There is a strong force of attraction between the appositively charged ions, so a lot of heat energy is required to break this force of attraction and melt the ionic compounds. This is why ionic compounds have high melting points.
Question : 24 A man went door to door posing as a goldsmith. He promised to bring back the glitter of old and dull gold ornaments. An unsuspecting lady gave a set of gold bangles to him which he dipped in a particular solution. The bangles sparkled like new but their weight was reduced drastically. The lady was upset but after a futile argument the man beat a hasty retreat. Can you play the detective to find out the nature of the solution he had used?
Answer :
Aqua regia (By volume, this contains 3 parts of concentrated hydrochloric acid and 1 part of concentrated nitric acid) is the solution, which is used to sparkle the bangles like new, but their weight will be reduced drastically.
Question : 25 Write equations for the reactions of (i) iron with water (ii) calcium and potassium with water
Answer :
(i) Iron reacts with steam to form magnetic oxide of Fe with the liberation of H2.
3Fe (s) + 4H2O(g) ——→ Fe3O4(s) + H2O (g)
(ii) Calcium reacts with water to form calcium hydroxide and hydrogen.
Ca(s) + 2H2O (l) ——→ Ca(OH)2 (aq) + H2(g)
Potassium reacts with cold water violently immediately with evolution of H2 which catches fire.
2K(s) + 2H2O(l) ——→ 2KOH(aq) + 2H2(g)
Question : 26 What would you observe when zinc is added to a sodium of iron(II) sulphate? Write the chemical reaction that takes place?
Answer :
Zinc is more reactive (more electro positive) than iron. Therefore it displaces iron from its salt solution. The colour of ferrous sulphate is pale green which becomes colourless.
FeSO4 + Zn ——→ ZnSO4 + Fe(s)
Light green Zinc Sulphate
Question : 27
Pratyush took sulphur powder on a spatula and heated it. He collected the gas evolved by inverting a test-tube over the burning sulphur.
What will be the action of this gas on:
Dry litmus paper?
Moist litmus paper?
Write a balanced chemical equation for the reaction taking place.
Answer :
a) When sulphur is brunt in air then sulphur dioxide gas is formed.
(i) Sulphur dioxide gas has no action on dry litmus paper.
(ii) Sulphur dioxide gas turns moist blue litmus paper to red.
b) S(s) + O2(g) → SO2(g)
Multiple Choice Questions
Question : 1. What is the colour of aqueous solution of CuSO4 and FeSO4 as observed in the laboratory?
(a) CuSO4 – blue; FeSO4 – light green
(b) CuSO4 – blue; FeSO4 – dark green
(c) CuSO4 – green; FeSO4 – blue
(d) CuSO4 – green; FeSO4 – colourless
Answer :
(a) Colour of CuSO4 solution is blue and FeSO4 solution is light green.
Question : 2. A student took four test tubes I, II, III and IV containing aluminium sulphate, copper sulphate? ferrous sulphate and zinc sulphate solutions respectively. He placed an iron strip in each of them.
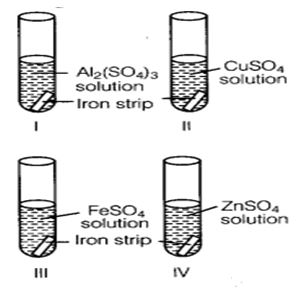
(a) I
(b) II
(c) III
(d) IV
Answer :
(b) In test tube II, because Fe is more reactive than copper but less reactive than Al arid Zn.
Question : 3. Aluminium sulphate and copper sulphate solutions were taken in two test tubes I and II respectively. A few pieces of iron filings were then added to both the solutions. The four students A, B, C and D recorded their observations in the form of a table as given below:
| Student | Al2(SO4)3 solution (I) | CuSO4 solution (II) |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Colourless solution → Light green | Blue colour is retained |
| 2 | Colourless solution → No change | Blue colour solution → Green |
| 3 | Colourless solution → Light blue | Blue colour solution → Green |
| 4 | No change in colour | Blue colour of solution fades |
Which student has recorded the correct observation?
(a) D
(b) C
(c) B
(d) A
Answer :
(c) Student B
Iron does not react with Al2(SO4)3 solution because iron is less reactive than aluminium. But Fe being more reactive than Cu displaces Cu from CuSO4 solution.
Question : 4. Aqueous solutions of zinc sulphate and iron sulphate were taken in test tubes I and II by four students A, B, C and D. Metal pieces of iron and zinc were dropped in the two solutions and observations made after several hours were recorded in the form of table as given below:
| Student Solution | Metal | Solution | Colour change Deposit/coating of solution | Deposit/coating obtained |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | Fe | ZnSO4 | Turned green | Silvery grey deposit |
| Zn | FeSO4 | No change | No change | |
| B | Fe | ZnSO4 | No change | Black deposit |
| Zn | FeSO4 | Colour faded | Grey coating | |
| C | Fe | ZnSO4 | No change | No change |
| Zn | FeSO4 | Turned colourless | Black deposit | |
| D | Fe | ZnSO4 | No change | Grey deposit |
| Zn | FeSO4 | No change. | Black deposit |
Which student has given the correct report?
(a) B
(b) D
(c) A
(d) C
Answer :
(d) Student C
(i) Fe is less reactive than zinc. So, Fe(s) + ZnSO4 (aq) ——→ No reaction (ii) Zn is more reactive than Fe, so it displaces iron as follows: Zn(s) + FeSO4 (aq) ——→ Fe(s) + ZnSO4 (aq) Zinc green Black deposit Colourless
Question : 5. 2 mL each of cone.HCl, cone.HNO3 and a mixture of cone.HCl and cone. HNO3 in the ratio of 3 : 1 were taken in test tubes labelled as A, B and C. A small piece of metal was put in each test tube. No change occurred in test tubes A’and Bbut the metal got dissolved in test tube C. The metal could be [NCERT Exemplar]
(a) Al
(b) Au
(c) Cu
(d) Pt
Answer :
(b, d) A mixture of cone. HCl and cone. HNO3 in the ratio of 3 : 1 is known as aqua-regia. Gold (Au) and platinum (Pt) dissolve only in aqua-regia as these metals are very less reactive.
Question : 6. When an aluminium strip is kept (a) Green solution of FeSO4 slowly turns brown
(b) Green solution of FeSO4 rapidly turns brown
(c) No change in colour of FeSO4
(d) Green solution of FeSO4 slowly turns colourless
Answer :
(a) The green solution of ferrous sulphate slowly turns brown. As aluminium is more reactive than iron, it displaces iron from ferrous sulphate solution.
Question : 7. Aluminium is used for making cooking utensils. Which of the following properties of aluminium are responsible for the same?
(i) Good thermal conductivity
(ii) Good electrical conductivity
(iii) Ductility
(iv) Flight melting point [NCERT Exemplar]
(a) (i) and (ii)
(b) (i) and (iii)
(c) (ii) and (iii)
(d) (i) and (iv)
Answer :
(d) Good thermal conductivity, malleability, light weight and high melting point are the properties/of aluminium due to which it-is used for making cooking utensils.
Question : 8. If copper is kept open in air, it slowly loses its shining brown surface and gains a green coating. It is due to the formation of [NCERT Exemplar]
(a) CuSO4
(b) CuCO3
(c) CU(NO3)2
(d) CuO
Answer :
(b) Copper reacts with CO2 present in air and forms a green coating on its surface due to the formation of basic copper carbonate [CuCO3.Cu(OH)2] as:
2Cu + O2+ CO2 + H2O——→ CuCO3.Cu(OH)
Additional Questions
Question : 1
a) Due to which property of metals are metallic foils prepared?
b) Write uses of aluminium foils
Answer :
a) Metallic foils are prepared, making use of the malleable property of metals.
b) Aluminium foils are used for
(i) wrapping chocolates and food stuff
(ii) to prepare hydrogen.
Question : 2 Name one non-metal and one metal, which are in liquid state at room temperature.
Answer :
Bromine is the non–metal and mercury is the metal which are in liquid state at room temperature.
Question : 3
Give reasons for the following
i) Zinc oxide is considered an amphoteric oxide.
ii) Non-metals in general do not displace hydrogen from dilute acids.
iii) Metals conduct electricity.
Answer :
i) Zinc oxide is considered an amphoteric oxide because it shows both acidic and basic behaviour.
ii) Non-metals do not react with dilute acids hence do not displace hydrogen from dilute acids.
iii) That metals conduct electricity because they contain free electrons which can move easily through the metal and conduct electric current.
Question : 4
Identify the following oxides with neutral, acidic, basic and amphoteric oxides.
i) Al2O3
ii) MgO
iii) SO2
iv) CO;
v) Na2O
vi) N2O
vii) ZnO
viii) CO2
ix) SO3
x) CaO.
Answer :
Neutral oxides: CO; N2O
Acidic oxides: SO2; CO2; SO3
Basic oxides: MgO; Na2O; CaO
Amphoteric oxides: Al2O3ZnO
Question : 5
By what processes do you concentrate the following ores:
i) PbS(galena)
ii) Fe2O3(haematite)
iii) Al2O3.2H2O (bauxite).
Answer :
i) PbS (galena) is concentrated by froth floatation method.
ii) Fe2O3 (haematite) is concentrated by magnetic separation.
iii) Al2O3.2H2O (bauxite) is concentrated by leaching process (chemical method).
Question : 6 Why is that iron does not occur as a metal in the crust of the earth? What are the common compound forms in which iron occurs? Which of these is more often used for extracting iron? Why are carbon and limestone mixed with iron ore before feeding it into the blast furnace? Write the chemical equations for the reduction step and the slag formation step.
Answer :
Iron is quite reactive and so it does not occur as a metal in the crust of the earth. The common compounds formed are its oxide, a carbonate and a sulphide. The oxide ore of iron called haematite is more often used for extracting iron. The carbon and limestone which is mixed with iron ore is called the charge. This charge is responsible for the formation of iron metal. Coke acts the reducing agent and addition of limestone helps to remove the earthy impurities like sand from the blast furnace by forming fusible slag.
Reduction of Iron(III)oxide or haematite to Iron: carbon monoxide reduces iron(III)oxide to iron metal
Fe2O3 + 3CO (g) → 2Fe + 3CO2 (g)
1: In the blast furnace limestone decomposes to form calcium oxide and carbon oxide.
CaCO3 (S) → CaO(s) + CO2 (g)
2: This calcium oxide reacts with sand and form molten calcium silicate called slag.
CaO (s) + SiO2→ CaSiO3(I)
slag
Question : 7
By what chemical processes do you obtain the following metals?
i) Mercury from HgO
ii) Iron from Fe2O3
iii) Manganese from MnO2
iv) Sodium form NaCl v) Aluminium from Al2O3.
Answer :
i) Mercury from Murcuric Oxide can be obtained by simple heating.
2HgO → 2Hg + O2
ii) Iron from Iron Oxide (Fe2O3) can be obtained by carbon reduction method i.e. heating with coke.
2C + O2→ 2CO
Fe2O3 + 3CO → 2Fe + 3CO2
iii) Manganese from manganesedioxide is obtained by alumina thermite process, i.e. heating with aluminium
3MnO2 + 4Al → 2Al2O3 + 3Mn
iv) Sodium from sodium chloride is obtained by electrolytic reduction (electrolysis) of fused NaCl.
NaCl← → Na+ + Cl–
At anode 2Cl–→ Cl2 + 2e–
At Cathode 2[Na– + e–→ Na]
v) 2Al2O3←→ 2Al3+ + 3(O)2-
At cathode 4[2Al3+ + 6(e) → 2Al]
At cathode 6O2-→ 3O2 + 12 e–
Question : 8
i) What is the composition of molten slag, formed in the extraction of iron in the blast furnace?
ii) What is the use of slag?
Answer :
i) Molten slag in the extraction of iron is calcium silicate(CaSiO3).
ii) Slag is used for constructions of roads.
Question : 9 Write the name of the compound, when iron is corroded?
Answer :
When iron is corroded rust is formed which is hydrated iron (III) oxide (Fe2O3.x.H2O)
Question : 10
Give reasons for the following
i. Na, K and Ca metals form hydrides by combination with hydrogen gas, but most other metals do not.
ii. Aluminium easily combines with oxygen but still it can be used for making kitchen utensils.
Answer :
i. Metals like Na, K and Ca can force the hydrogen atoms to accept electrons given by them and form hydrides.
ii. Aluminium forms a protective oxide layer when it combines with oxygen and hence it is used for making kitchen utensils.
Question : 11 i) Among iron and aluminium which rusts easily? ii) What are the conditions, necessary for rusting of iron?
Answer :
i) Among iron and aluminium, iron rusts easily. It forms Al2O3. That is why iron pipes are wrapped with aluminium metal to prevent rusting of iron.
ii) 1) Air or oxygen 2) Water, containing dissolved air. These are necessary conditions for rusting of iron.
Question : 12 Name an ore of zinc other than zinc oxide. By what process can this ore be converted to zinc oxide.
Answer :
Zinc blende(ZnS) is an ore of zinc other than zinc oxide. Roasting is the process by which ZnS can be converted into zinc oxide.
Question : 13
What property of hydrogen is observed in the following experiments?
i) Balloon, filled with hydrogen, floats.
ii) Pop sound is heard when a burning splint is introduced at the mouth of hydrogen filled jar.
iii) When black cupric oxide is heated in a stream of hydrogen, reddish colour is obtained.
Answer :
i) Hydrogen is light. So hydrogen filled balloons float.
ii) Pop sound is due to the combustible property of hydrogen. Hydrogen burns with oxygen at the mouth of the hydrogen filled jar.
iii) Hydrogen has reducing property. Hence it reduces black cupric oxide to red copper metal.
Question : 14
Select the non-metals amongst the following
i) Bismuth ii) Sulphur iii) Arsenic iv) Hydrogen.
Answer :
Hydrogen and Sulphur are the non-metals.
Question : 15 How do you test ammonia gas?
Answer :
Ammonia gas is tested, by showing a drop of conc. HCl by means of a glass rod to it, when dense white fumes of ammonium chloride are formed.
Ammonium chloride (dense white fumes).
Question : 16
Write chemical equations for reactions taking place when
i) Cinnabar is heated in air.
ii) Concentrated sulphuric acid and sulphur are heated together. Calcium metal reacts with water.
Answer :
I) Cinnabar is heated in air
2HgS + 3O2 (g) → 2Hg)(s) + SOs
II) Calcium metal reacts with water.
Ca(s) + 2H2O (l) → Ca(OH)2 (aq) + H2(g)
Question : 17 What are the uses of ammonia?
Answer :
i) Ammonia is used in the manufacture of fertilizers like ammonium sulphate and ammonium nitrate.
ii) To manufacture nitric acid by Ostwald’s process.
iii) To prepare dyes, explosives, cellulose acetate etc.
Question : 18 Why do some metals like, Na, K, Ca, Mg not occur in nature as free elements?
Answer :
Metals like Na, K, etc (alkali metals) and Ca, Mg etc (alkaline earth metals) are very reactive and hence they react with atmospheric oxygen and carbon dioxide and also with other non-metals like sulphur present in the earth’s crust to form compounds like oxides, carbonates, sulphides, sulphates and chlorides. So they do not occur in free state, but are found in the form of the above compounds.
Question : 19
Write chemical equations for reactions taking place when:
i) Manganese dioxide is heated with aluminium powder.
ii) Steam is passed over hot iron.
iii) A mixture of ammonia and oxygen is passed over platinum heated to 1073 K.
Answer :
i) Manganese dioxide is heated with aluminium powder.
3MnO2 + 4Al (s) → 3Mn(l) + Al2O3
ii) Steam is passed over hot iron.
3Fe(s) + 4H2→ Fe2O3(s) + 4H2
iii) A mixture of ammonia and oxygen is passed over platinum heated to 1073K.
4NH3(g) + 5O2(g) → 4NO(g) + 6H2O
Question : 20 Why are metals like sodium, calcium, magnesium, aluminium etc. obtained by electrolytic reduction?
Answer :
Metals like Na, Ca, Mg, Al etc. which are high up in the activity series are electropositive elements and possess a high affinity for oxygen. So their oxides are very much stable and cannot be reduced with common reducing agents like carbon. So carbon reduction process cannot be applied to prepare these metals. They can only be prepared by electrolytic reduction of their fused chlorides or oxides.
Question : 21 State briefly how you will extract iron from its ore. Draw a neat and labelled diagram. Write all the chemical reactions involved in it.
Answer :
Iron is usually extracted from its chief ore, Haematite.
The various steps involved in the production of iron metal from haematite are as follows:
1. Concentration of ore
The concentration of haematite or is done by the method of hydraulic washing. The ore is spilt into small pieces and then washed in a stream of water to remove sand, clay. In this way ,a fairly concentrated ore is obtained and usually there is no need of any further concentration.
2. Calcination
The washed iron ore is then strongly heated in the absence of air to expel water sticking to it.
3. Reduction
The washed and dried ore is mixed with weighed quantities of coke and limestone and put into a blast furnace from the top .A blast of hot air is blown into the furnace from near its bottom. This air is to supply for the burning of coke.
The two reactions which take place in the blast furnace leading to the formation of iron metal are: formation of carbon monoxide and reduction of haematite.
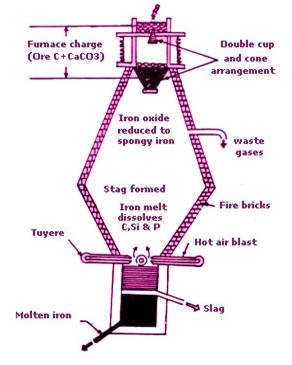
Carbon monoxide is the main reducing agent in the extraction of iron by blast furnace. Carbon monoxide is formed from coke in two steps:
Near the bottom of the furnace code burns in air to form carbon dioxide and a lot of heat is produced. C(s) + O2→ CO2 + Heat
In the center of the furnace, carbon dioxide reacts with white hot coke to form carbon monoxide.
CO2 + C(s) → 2CO
2) Reduction of Iron (III) oxide to Iron.
In the upper part of the furnace, carbon monoxide reduces iron (III) oxide to iron metal .
Fe2O3 + 3CO → 2Fe(I) + 3CO2(g)
Iron metal is produced as a grey solid which melts as it comes down in the furnace where the temperature is very high. Molten iron collects at the bottom of the furnace.
Question : 22
Write the chemical formula for the following.
a) Alumina b) Silica c) Rust d) Oleum e) Slag f) Sodium amalgam g) Bauxite h) Haematite.
Answer :
a) Alumina – Al2O3
b) Silica– SiO2
c) Rust– Fe2O3. xH2O
d) Oleum– H2S2O7 (SO3, dissolved in H2SO4)
e) Slag– CaSiO3
f) Sodium amalgam– Na – Hg (an alloy of sodium with mercury)
g) Bauxite– Al2O3.2H2O
h) Haematite– Fe2O3
a) Alumina – Al2O3
b) Silica – SiO2
c) Rust – Fe2O3. xH2O
d) Oleum – H2S2O7 (SO3, dissolved in H2SO4)
e) Slag – CaSiO3
f) Sodium amalgam – Na – Hg (an alloy of sodium with mercury)
g) Bauxite – Al2O3.2H2O
h) Haematite – Fe2O3
Question : 23 In Frasch process of digging out sulphur from a deep underground, how has it made possible to life sulphur from the bed to surface of each? What is the basic principle on which extraction of sulphur is based? Draw a neat and labelled diagram. Besides elemental form, in what compound forms is sulphur found. Give two physical properties of sulphur.
Answer :
In the Frasch process in order to bring out sulphur from the underground deposits, a hole of about 30 cm diameter is bored up to the sulphur bed. It is based on the principle that sulphur has a comparatively low melting point of 115o or 388o due to which it can be melted by introducing super-heated water in the underground sulphur deposits. This mixture of molten sulphur and water is then brought out by the force of hot, compressed air.
Three concentric pipes A, B, C of different diameters are put down in the boring.
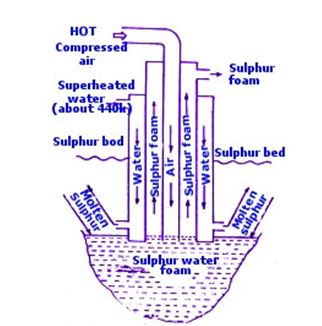
Question : 24
The copper vessels used in homes are found to be coated with green colour. Answer the following.
a) What is the chemical composition of the green coating?
b) Why do copper vessels form such a green coating?
c) What is the name of the phenomenon, responsible for the green coating?
d) Copper vessels are best cleaned with tamarind or lemon juice, but not with soap. Why?
Answer :
a) Green coloured coating on copper is due to the formation of basic copper carbonate, CuCO3.Cu(OH)2.
b) Copper forms green coating of basic copper carbonate as it reacts with water, atmospheric oxygen and carbon dioxide.
c) Corrosion phenomenon is responsible for the formation of basic copper carbonate (green).
d) Since basic copper carbonate is basic in nature, it can be removed by tartaric acid present in tamarind or citric acid, present in lemon. Soap is basic in nature. So copper vessels are best cleaned with tamarind or lemon.
Question : 25
Give reasons for the following
i. Silicon counts among metalloids
ii. Carbon is not used for making aluminium from aluminium oxide.
iii. For making hydrogen by reaction with hydrochloric acid, granulated zinc is preferred to a block of zinc.
Answer :
i. Silicon shows properties of both metals and non-metals and hence silicon counts among metalloids.
ii. Carbon has less affinity for oxygen than Aluminium and hence it cannot eliminate oxygen from Aluminium oxide.
iii. Zinc granules are preferred to a block of zinc because it offers a large surface area for the reaction with the acid.
Question : 26 Explain
i) Why sugar chars (turns black) when conc. H2SO4 is added to it?
ii) What is the blue colour of crystalline copper sulphate due to?
Answer :
Concentrated H2SO4
C12H22O11→ 12C(s) + 11H2O(I)
ii) Blue colour of crystalline copper sulphate is due to five water molecules of hydration in CuSO4 5H2O.
Question : 27
Write chemical equations for reactions taking place when
i. Zinc carbonate is calcined.
ii. Ammonia gas is passed over heated copper (II) oxide.
Answer :
(i) ZnCO3→ ZnO + CO2
(ii) 3CuO(s) + 2NH3→ Cu(s) + N2(g) + 3H2O
Question : 28
(i) What is the colour of potassium dichromate solution?
(ii) What is the colour of Cr3+ ion?
(iii) What property of SO2 is responsible for bringing change of colour of potassium dichromate?
Answer :
(i) Potassium dichromate solution is orange yellow colour.
(ii) The colour of Cr3+ ion is green.
(iii) Reducing property of sulphur dioxide is responsible to change the orange yellow colour of K2Cr2O7 to green colour.
Question : 29 How is chloride of lime chemically different from calcium chloride? Why does chloride of lime gradually lose its chlorine when kept exposed to air?
Answer :
Chemically, chloride of lime is calcium oxy chloride, CaOCl2, also called bleaching powder. When exposed to air it gradually lose its chlorine because it reacts with carbon dioxide present in air to produce calcium carbonate and chlorine gas.
Question : 30 Write short notes on the bleaching action of sulphur dioxide.
Answer :
a) Sulphur dioxide bleaches the vegetable colours in the presence of moisture.
b) It bleaches the vegetable colours by reduction. It removes oxygen from coloured material.
c) Its bleaching action is temporary, because atmospheric oxygen again oxidises the bleached article back to its original colour.
d) SO2 is used to bleach delicate fabrics like wool, silk etc.
Question : 31
(a) What is the atomicity of sulphur?
(b) How do you bring the change of rhombic sulphur to monoclinic sulphur and vice versa?
(c) What is the action of conc. HNO3 on sulphur?
Answer :
(a) Atomicity of sulphur is 8. Its formula is S8.
(b) Rhombic sulphur, when heated to above 369K, changes to monoclinic sulphur. Monoclinic sulphur, on cooling to below 369 K reverts back to rhombic sulphur.
Above 369 K
Rhombic sulphur 噒 Monoclinic sulphur
Below 369 K
(c )Conc.HNO3 oxidises sulphur to sulphuric acid while the former is reduced to NO2
S(s) + 6HNO3(Aq) → H2SO4 + 6NO2 + 2H2O(l)
Question : 32 Name two metals used in making fuse wires.
Answer :
Copper and Aluminium are the two metals used in making fuse wires.
Question : 33
(i) How can ammonia be converted to NO2 and nitric acid?
(ii) What is liquor ammonia?
Answer :
(I) When ammonia is oxidised by heating with oxygen to 1073 K in the presence of platinum gauze, reddish brown vapours of NO2 are formed
1073K
4NH3 + 5O2 ———→ 4NO + 6H2O
Pt guaze as catalyst
2NO + O2———→ 2NO2
When NO2 dissolves in water, nitric acid is formed.
2NO2 + H2O + O → 2HNO3
Thus HNO3 is manufactured from ammonia.
(iii) A saturated solution of ammonia is known as liquor ammonia.
Question : 34
Complete the following reactions
CH3COOC2H5 + NaOH ———→ ………………………………………
CrO3
CH3CH2OH ———→ ………………………………..
Answer :
CH3COOC2H5 + NaOH→ CH
3COONa + C2H5OH
CrO3
CH3CH2OH —→ CH3CHO + H2O
Question : 35
Define the following terms
i) Mineral
ii) Ore
iii) gangue.
Answer :
i) The inorganic elements or compounds which occur naturally in the earth’s crust are known as minerals.
ii) The minerals from which a metal can be profitably extracted are called ores.
iii) The impurity of sand and rocky materials present in the ore is known as gangue.
Question : 36
a) State why hydrogen is said to be a clean fuel?
b) What property of hydrogen is involved in being a good fuel?
c) What is hydrogenation of oils? Write one application.
Answer :
a) Hydrogen is a clean fuel because its reaction with oxygen produces only water. It does not form gases like CO2, NO2 etc, which pollute air.
b) Hydrogen, on combustion with oxygen, produces water and a lot of heat. This is an exothermic reaction.
c) Oils are unsaturated molecules, containing double bond. So hydrogen atoms are added at the double bonds of the molecules of oil. The reaction of hydrogen with oils is known as hydrogenation. The hydrogenation reaction takes place at 473 K and in the presence of nickel catalyst.
Vanaspati or dalda ghee is prepared by hydrogenation of vegetable oils.
Question : 37 What is the formula of Ammonia? Write the flow diagram for the manufacture of ammonia by Haber’s process. State any two of its physical properties. Write the equation for its reaction with HCl.
Answer :
The formula of Ammonia is NH3.
The flow diagram of the manufacture of ammonia by Haber’s process is given below:
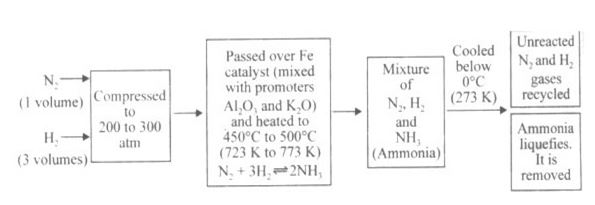
1. Ammonia is a colourless gas having a characteristic pungent smell.
2. Ammonia is highly soluble in water.
Question : 38 How do metals react with hydrogen? Explain with an example.
Answer :
Only very few reactive metals like sodium, potassium, calcium and magnesium react with hydrogen to form metal hydrides. Example when hydrogen gas is passed overheated sodium, sodium hydride is formed.
Question : 39 Name a metal which is stored in kerosene oil.
Answer :
Sodium is a metal which is stored in kerosene oil.
Question : 40 Metals are electropositive in nature. Explain.
Answer :
Metals are electropositive in nature because they can form positive ions by the loss of electrons.
Question : 41 Explain the displacement of hydrogen by a metal from an acid with an example. Give the equation to support the same.
Answer :
2Na(s) + 2HCl (aq) → 2NaCl (aq) + H2 (g)
Question : 42 Why is sodium kept in kerosene?
Answer :
Sodium reacts so vigorously that they catch fir if it is kept in the open air and hence sodium is kept in kerosene.
Question : 43 Name the element or compound which is associated with Hall’s process.
Answer :
Aluminium is associated with Hall’s process.
Question : 44 Which metal is used in nuclear reactors and aerospace projects?
Answer :
Aluminium is used in nuclear reactors and aerospace projects.