Class 6 - Mathematics : Practical Geometry
Exercise : 14.5

Top Block 1
NCERT Solutions Class 6 Mathematics Practical Geometry Ex 14.5
Question: 1.Draw AB of length 7.3 cm and find its axis of symmetry.
Answer :
Axis of symmetry of line segment AB will be the perpendicular bisector of AB. So, draw the perpendicular bisector of AB.
Steps of construction:
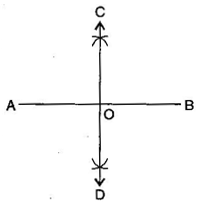
(ii) Taking A and B as centres and radius more than half of AB, draw two arcs which intersect each other at C and D.
(iii) Join CD. Then CD is the axis of symmetry of the line segment AB.
Question: 2.Draw a line segment of length 9.5 cm and construct its perpendicular bisector.
Answer :
Steps of construction:
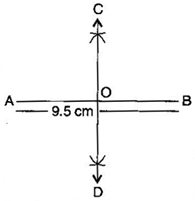
Mddle block 1
(ii) Taking A and B as centres and radius more than half of AB, draw two arcs which intersect each other at C and D.
(iii) Join CD. Then CD is the perpendicular bisector of AB.
Question: 3.Draw the perpendicular bisector of XY whose length is 10.3 cm.
(a) Take any point P on the bisector drawn. Examine whether PX = PY.
(b) If M is the mid-point of XY, what can you say about the lengths MX and XY?
Answer :
Steps of construction:

(ii) Taking X and Y as centres and radius more than half of AB, draw two arcs which intersect each other at C and D.
(iii) Join CD. Then CD is the required perpendicular bisector of XY.
Now:
(a) Take any point P on the bisector drawn. With the help of divider we can check that PX = PY.
(b) If M is the mid-point of XY, then MX = 12XY.
Question: 4.Draw a line segment of length 12.8 cm. Using compasses, divide it into four equal parts. Verify by actual measurement.
Answer :
Steps of construction:
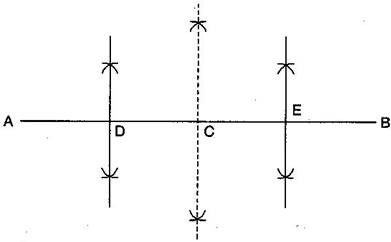
(ii) Draw the perpendicular bisector of AB which cuts it at C. Thus, C is the mid-point of AB.
(iii) Draw the perpendicular bisector of AC which cuts it at D. Thus D is the mid-point of .
(iv) Again, draw the perpendicular bisector of CB which cuts it at E. Thus, E is the mid-point of CB.
(v) Now, point C, D and E divide the line segment AB in the four equal parts.
(vi) By actual measurement, we find that
AD = DC = CE = EB = 3.2 cm
Question: 5.With PQ of length 6.1 cm as diameter, draw a circle.
Answer :
Steps of construction:
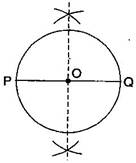
(ii) Draw the perpendicular bisector of PQ which cuts, it at O. Thus O is the mid-point of PQ.
Taking O as centre and OP or OQ as radius draw a circle where diameter is the line segment PQ.
Question: 6.Draw a circle with centre C and radius 3.4 cm. Draw any chord AB. Construct the perpendicular bisector AB and examine if it passes through C.
Answer :
Steps of construction:
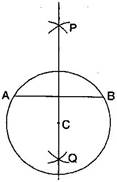
(ii) Draw any chord AB.
(iii) Taking A and B as centers and radius more than half of AB, draw two arcs which cut each other at P and Q.
(iv) Join PQ. Then PQ is the perpendicular bisector of AB.
This perpendicular bisector of AB passes through the centre C of the circle.
Question: 7.Repeat Question: 6, if AB happens to be a diameter.
Answer :
Steps of construction:
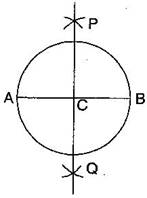
(ii) Draw its diameter AB.
(iii) Taking A and B as centers and radius more than half of it, draw two arcs which intersect each other at P and Q.
(iv) Join PQ. Then PQ is the perpendicular bisector of AB.
We observe that this perpendicular bisector of AB passes through the centre C of the circle.
Question: 8.Draw a circle of radius 4 cm. Draw any two of its chords. Construct the perpendicular bisectors of these chords. Where do they meet?
Answer :
Steps of construction:
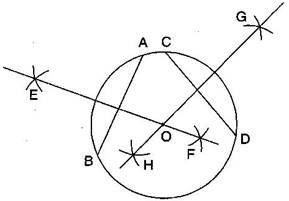
(ii) Draw any two chords AB and CD in this circle.
(iii) Taking A and B as centers and radius more than half AB, draw two arcs which intersect each other at E and F.
(iv) Join EF. Thus EF is the perpendicular bisector of chord CD.
(v) Similarly draw GH the perpendicular bisector of chord CD.
These two perpendicular bisectors meet at O, the centre of the circle.
Question: 9.Draw any angle with vertex O. Take a point A on one of its arms and B on another such that OA = OB. Draw the perpendicular bisectors of OA and OB. Let them meet at P. Is PA = PB?
Answer :
Steps of construction:

(ii) Take a point A on one of its arms and B on another such that
(iii) Draw perpendicular bisector of OA and OB.
(iv) Let them meet at P. Join PA and PB.
With the help of divider, we check that PA = PB.
