Class 10 - Science
Chapter 6 - Life Processes

Top Block 1
Question : 1 How are fats digested in our bodies? Where does this process take place?
Answer :
The small intestine is the site of the complete digestion of carbohydrates, proteins and fats. It receives the secretions of the liver and pancreas for this purpose. The food coming from the stomach is acidic and has to be made alkaline for the pancreatic enzymes to act. Bile juice from the liver accomplishes this in addition to acting on fats. Fats are present in the intestine in the form of large globules, which make it difficult for enzymes to act on them. Bile salts break them down into smaller globules increasing the efficiency of enzyme action. The pancreas secretes pancreatic juice, which contains enzymes like trypsin for digesting proteins and lipase for breaking down emulsified fats. The walls of the small intestine contain glands, which secrete intestinal juice. The enzymes present in it finally convert the proteins to amino acids, complex carbohydrates into glucose and fats into fatty acids and glycerol.
Question : 2 What is the role of saliva in the digestion of food?
Answer :
When we eat something we like, our mouth ‘waters’. This is actually not only water, but also a fluid called saliva secreted by the salivary glands. Another aspect of the food we ingest is its complex nature. If it is to be absorbed from the alimentary canal, it has to be broken into smaller molecules. This is done with the help of biological catalysts called enzymes. The saliva contains an enzyme called salivary amylase that breaks down starch, which is a complex molecule to give sugar. The food is mixed thoroughly with saliva and moved around the mouth while chewing by the muscular tongue.
Question : 3 What are the necessary conditions for autotrophic nutrition and what are its by-products?
Answer :
Carbon and energy requirements of the autotrophic organism are fulfilled by photosynthesis. It is the process by which autotrophs take in substances from the outside and convert them into stored forms of energy. This material is taken in the form of carbon dioxide and water, which is converted into carbohydrates in the presence of sunlight and chlorophyll. Carbohydrates are utilised for providing energy to the plant. The carbohydrates, which are not used immediately, are stored in the form of starch, which serves as the internal energy reserve to be used as and when required by the plant.
Question : 4 What are the differences between aerobic and anaerobic respiration? Name some organisms that use the anaerobic mode of respiration.
Answer :
The food material taken in during the process of nutrition is used in cells to provide energy for various life processes. Diverse organisms do this in different ways – some use oxygen to breakdown glucose completely into carbon dioxide and water; some use other pathways that do not involve oxygen. In all cases, the first step is the breakdown of glucose, a six-carbon molecule, into a three-carbon molecule called pyruvate. This process takes place in the cytoplasm. Further, the pyruvate may be converted into ethanol and carbon dioxide. This process takes place in yeast during fermentation. Since this process takes place in the absence of air (oxygen), it is called anaerobic respiration. Breakdown of pyruvate using oxygen takes place in the mitochondria. This process breaks up the three-carbon pyruvate molecule to give three molecules of carbon dioxide. The other product is water. Since this process takes place in the presence of air (oxygen), it is called aerobic respiration. The release of energy in this aerobic process is a lot greater than in the anaerobic process.
Question : 5 How are the alveoli designed to maximise the exchange of gases?
Answer :
Within the lungs, the passage divides into smaller and smaller tubes, which finally terminate in balloon-like structures, which are called alveoli. The alveoli provide a surface where the exchange of gases can take place. The walls of the alveoli contain an extensive network of blood vessels. As we have seen in earlier years, when we breathe in, we lift our ribs and flatten our diaphragm, and the chest cavity becomes larger as a result. Because of this, air is sucked into the lungs and fills the expanded alveoli. The blood brings carbon dioxide from the rest of the body for release into the alveoli, and the oxygen in the alveolar air is taken up by blood in the alveolar blood vessels to be transported to all the cells in the body. During the breathing cycle, when air is taken in and let out, the lungs always contain a residual volume of air so that there is sufficient time for oxygen to be absorbed and for the carbon dioxide to be released.
Question : 6 Describe double circulation in human beings. Why is it necessary?
Answer :
The double circulatory system of blood flow refers to the separate systems of pulmonary circulation and the systemic circulation.
The adult human heart consists of two separated pumps, the right side with the right atrium and ventricle which pumps deoxygenated blood into the pulmonary circulation.
The oxygenated blood re-enters the left side of the heart through the pulmonary vein into the left atrium and passes to the left ventricle where it is pumped to the rest of the body. This part of the circulation is called as systemic circulation. This type of circulation is called double circulation. The advantage of a double circulatory system is that blood can be pumped to the rest of the body at a higher pressure.
Multiple Choice Questions
Question : 1. Yeast respires anaerobically using sugar as a substrate. Out of the options given below, choose the correct combination of condition and product?
| Condition | Product | |
|---|---|---|
| a | Aerobic | Alcohol |
| b | Aerobic | Lactic acid |
| c | Anaerobic | Alcohol |
| d | Anaerobic | Lactic acid |
Answer :
(c) Under an aerobic condition, yeast respires and converts glucose to alcohol and CO2.
Question : 2. The table shows the percentage composition of four samples of air. Which sample could have been breathed out by a person after vigorous exercise?
| Samples | Oxygen | Carbondioxide | Water Vapour |
|---|---|---|---|
| a | 16 | 0.3 | Saturated |
| b | 16 | 4 | Saturated |
| c | 21 | 0.03 | Trace |
| d | 21 | 3 | Trace |
Answer :
(b) This is because rapid aerobic respiration occurs – during vigorous exercise in order to obtain more energy.
Question : 3. Cramps caused during sudden activities are due to the formation of
(a) lactic acid
(b) acetic acid
(c) excess of water
(d) ethanol
Answer :
(a) Lactic acid is formed by the breakdown of pyruvate when oxygen is insufficient in muscles instead of forming C02 and water. Accumulation of excess lactic acid in the muscles causes cramps.
Question : 4. Which of the following plays nose like function in plants?
(a) Flower
(b) Phloem
(c) Stomata
(d) Chlorophyll
Answer :
(c) Stomata are pores which help in the passage of air in the plants.
Question : 5. Which changes occur when a person breathe in deeply?
| Diaphragm Muscle | External Intercostal Muscles | |
|---|---|---|
| a | Contracts | Contract |
| b | Contracts | No change |
| c | Relaxes | Contract |
| d | Relaxes | Relax |
Answer :
(a) When a person breathes deeply the external intercostal muscles contract causing the rib cage to swing up and out. Also, the diaphragm contracts and flattens causing the thoracic cavity to increase in volume and decrease in pressure.
Question : 6.
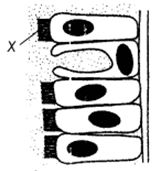
Mddle block 1
(a) Gaseous exchange
(b) Mucus removal
(c) Phagocytosis
(d) Secretion of mucus
Answer :
(b) The cilia (X) of the cells lining the air passages move in a sweeping motion to keep the air passages clean. The constant action of these cilia carry mucus and debris upward into the pharynx where they are swallowed.
Question : 7. The table given below shows the percentage composition of a gas in inspired and in expired air.
| %Composition | |
|---|---|
| Inspired Air | 21.0 |
| Expired Air | 16.0 |
What is the gas?
(a) Carbon dioxide
(b) Nitrogen
(c) Oxygen
(d) Water vapour
Answer :
(c) The gas is oxygen as atmospheric air has approximately 21% of oxygen
Additional Questions
Question : 1 Define nutrition? What are the different modes of nutrition?
Answer :
Nutrition is the process of intake, as well as utilization of nutrients by an organism. The different modes of nutrition are saprophytic nutrition, parasitic nutrition and holozoic nutrition.
Question : 2 What is the mode of nutrition in fungi?
Answer :
Saprophytic nutrition is the mode of nutrition that is seen in fungi.
Question : 3 Name the pigment, which can absorb solar energy.
Answer :
Chlorophyll is the pigment, which can absorb solar energy.
Question : 4 Name the two stages in photosynthesis.
Answer :
The two stages in photosynthesis are
(i) Light reaction and
(ii) Dark reaction.
Question : 5 Name the factors, which affect photosynthesis.
Answer :
The factors which affect photosynthesis, are light, water, temperature, humidity, age of the leaf and carbon dioxide.
Question : 6 Define a herbivore and a carnivore.
Answer :
The animals that feed only on plants are called herbivores. The animals that feed only on flesh are called carnivores.
Question : 7 How does amoeba engulf its food?
Answer :
Amoeba engulfs its food by extending pseudopodia. This process is known as Phagocytes.
Question : 8 Name the parts of the digestive system of a grasshopper.
Answer :
The parts of digestive system of a grasshopper are pharynx, salivary glands, hepatic caeca, Malpighian tubules, ileum, colon, rectum and anus.
Question : 9 What are the functions of the liver and the pancreas?
Answer :
The liver secretes bile, which contains bile pigments and bile salts. The bile secreted by the liver cells is normally stored in the gall bladder, until needed in the duodenum. Pancreas lies parallel to and beneath the stomach. It is a large gland, which secretes digestive enzymes as well as the hormones, insulin and glucagon. Both bile and pancreatic juice enter duodenum through a common duct. Bile emulsifies fat present in the food. Pancreatic juice contains trypsin, for digesting proteins and pancreatic amylase for the breakdown of starch.
Question : 10 Define breathing.
Answer :
Breathing is a process by which organisms inhale oxygen. The inhaled oxygen gets diffused into the blood and the carbon dioxide from the blood diffuses back into the alveoli from where it is exhaled.
Question : 11 How is respiration different from breathing?
Answer :
Respiration is a complex process, which includes breathing, the mechanism of exchange of gases,oxygen and carbon dioxide and oxidation of digested food occurring in the cells in order to release energy. The main outcome of respiration is the release of energy through oxidation of simple food molecules such as glucose.
Question : 12 In which kind of respiration is more energy released?
Answer :
In aerobic respiration more energy is released.
Question : 13 Which part of the roots is involved in exchange of respiratory gases?
Answer :
Root hair is the part of the root which is involved in exchange of respiratory gases.
Question : 14 What are (i) stomata and (ii) lenticels?
Answer :
(i) Stomata are tiny apertures found on the surface of the leaf, which regulate the exchange of respiratory gases and transpiration.
(ii) Lenticels are the raised pores in the woody plants that allow the exchange of gases between the atmosphere and the internal tissues.
Question : 15 Give two points of differences between respiration in plants and respiration in animals.
Answer :
The respiration in plants differ from respiration in animals in two respects, they are
(i) There is minimal transport of gases from one part of the plant to another, unlike the animals.
(ii) Plant respiration occurs at a much slower rate than animal respiration.
Question : 16 Name the respiratory organs of
(i) fish
(ii) mosquito
(iii) earthworm
(iv) dog
Answer :
The respiratory organs of
(i) fish – gills
(ii) mosquito – tracheoles
(iii) earthworm – skin
(iv) dog – lungs.
Question : 17
Answer :
The oxygen rich air enters through openings called spiracles situated on the sides of the body of an insect. Spiracles open into tracheal system. Trachea branch into tracheoles, which reach the cells. Thus, every cell gets oxygen directly. Carbon dioxide released by cells moves out through the spiracles.
Question : 18 From where do the following take in oxygen?
(i) prawn (ii) rat.
Answer :
(i) Prawns take in oxygen that is dissolved in water.
(ii) Rat takes in oxygen from the atmosphere.
Question : 19 State the function of epiglottis.
Answer :
Epiglottis prevents the food from entering into the trachea.
Question : 20
Answer :
The walls of trachea do not collapse when there is less air in it, because, they are supported by rings of cartilage.
Question : 21
Answer :
Nutrition is the sum of all those activities which are concerned with ingestion, digestion, absorption of digested food, egestion, oxidation of simple food to produce energy for growth, development and maintenance of living organism.
Question : 22
Answer :
Energy is required by an organism even during sleep because various biological processes keep on occurring in its body.
Question : 23 Define photolysis.
Answer :
The phenomenon of breaking down of water in the illuminated chloroplast is known as photolysis.
Question : 24 What are the living organisms that cannot make their own food called?
Answer :
The living organisms that cannot make their own food called heterotrophs.
Question : 25 What are chemotrophs?
Answer :
Chemotrophs are organisms, which do not require light. They manufacture their food from inorganic substances in the presence of energy derived from the oxidation of simple inorganic compounds of iron, sulphur, etc.
e.g. bacterium Nitrosamines.
What is compensation point?
Answer :
The compensation point is the amount of light on the light curve where the rate of photosynthesis exactly matches the rate of respiration. At this point, the uptake of CO2 through photosynthetic pathways is exactly matched to the respiratory release of carbon dioxide, and the uptake of O2 by respiration is exactly matched to the photosynthetic release of oxygen. This point is reached during early mornings and late evenings.
Other than chlorophyll
Question : which other pigment is necessary for photosynthesis?
Answer :
Carotenoids are the pigments, which are necessary for photosynthesis other than chlorophyll. Carotenoids are yellow, orange, red or brown pigments, which absorb sunlight and pass this energy on to chlorophyll for the purpose of photosynthesis. Thus, the carotenoids themselves do not carry out photosynthesis but help in photosynthesis.
Question : 28 Where does digestion begin?
Answer :
Digestion begins from the mouth.
Question : 29 What is the name given to the process of using the absorbed food for producing energy?
Answer :
The name given to the process of using the absorbed food for producing energy is assimilation.
Question : 30 What happens to visible light of the Sun when it falls on chlorophyll?
Answer :
Visible light of the Sun consists of seven colours, namely, violet, indigo, blue, green, yellow, orange and red. Out of these lights of different wave lengths, chlorophyll absorbs mainly blue, violet, red and orange lights but does not absorb the green light. It is due to the reflection of green light by the chlorophyll that the plant looks green in colour.